Retinal Surgery
The retina services available in our center include:
|
|
RETINAL TEAR AND RETINAL DETACHMENT
Retinal detachment is a very serious eye condition that happens when the retina separates from the underlying tissue. The retina cannot function when it is detached. It can lead to blindness if left untreated.
It is caused by vitreous gel at the posterior part of the eyeball) pulling at the retina, resulting in retinal holes or tears. If fluid from within the eye passes through a retinal hole or tear, that can separate the retina from its underlying tissue -- and that's retinal detachment.
Warning signs of retinal detachment include:
- Symptoms of flashes and floaters;
- Seeing a shadow across the field of vision. Retinal detachment often causes sudden loss of vision and may progress to total blindness in days or weeks.
Treatment
During the stage of retinal tear, before full detachment occurs, a simple office laser treatment or cryotherapy may be able to prevent the need for a more major retinal detachment operation. Surgery is required to repair a detached retina. Surgical procedures used to treat a retinal detachment include:
• Scleral buckling surgery
• Vitrectomy
• Pneumatic retinopexy
Some patients may need a combination of the procedures. Very often gas or silicone oil may be used as internal tamponade as part of the operation. Recovery may take up to 3 months before the final visual outcome is stable.

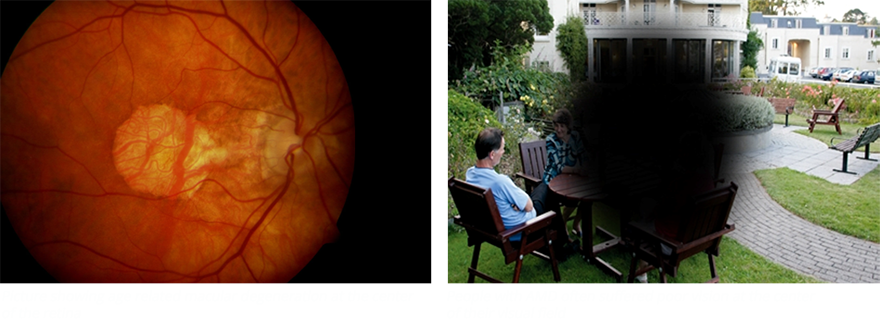
AGE RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD) causes vision loss in those aged over 50. It causes a gradual loss of central vision. Central vision is needed for detailed work and for things like reading and driving. There are two main types of AMD - 'wet' and 'dry'. 'Wet' AMD is most severe but more treatable. Normally, visual loss caused by AMD cannot be reversed however there are new medications which are able to delay the progression of visual loss.
Certain risk factors increase the risk of developing AMD. These include:
Stopping smoking and protecting the eyes from the sun's rays by wearing sunglasses are important. A healthy balanced diet rich in antioxidants may be beneficial, as may the addition of dietary supplements. Medical treatment include administration of specific medication via injection (anti-vascular endothelial growth factor), photodynamic therapy and laser photocoagulation therapy.
Certain risk factors increase the risk of developing AMD. These include:
- Smoking tobacco.
- Possibly, high blood pressure (inconclusive medical evidence at the moment).
- A family history of AMD. (AMD is not a straightforward hereditary condition. However, your risk of developing AMD is increased if it occurs in other family members.)
- Sunlight. This has yet to be proven, but laboratory studies suggest that the retina is damaged by sunlight rays (UVA and UVB rays).
SYMPTOMS OF AMD
- The main early symptom is blurring of central vision despite using your usual glasses.
- One specific early symptom to be aware of is visual distortion. Typically, straight lines appear wavy or crooked. For example, the lines on a piece of graph paper, or the lines between tiles in a bathroom, or the border of any other straight object, etc.
- A 'blind spot' then develops in the middle of your visual field. This tends to become larger over time as more and more rods and cones degenerate in the macula.
AMD is painless. Symptoms of dry AMD tend to take 5-10 years to become severe. However, severe visual loss due to wet AMD can develop more quickly.
Treatment for AMD
Stopping smoking and protecting the eyes from the sun's rays by wearing sunglasses are important. A healthy balanced diet rich in antioxidants may be beneficial, as may the addition of dietary supplements. Medical treatment include administration of specific medication via injection (anti-vascular endothelial growth factor), photodynamic therapy and laser photocoagulation therapy.


